Real-Time MRI
The following examples are real-time MRI movies that represent preliminary applications of our novel method to various physiological processes. All data have been acquired at a field strength of 3 T using a Siemens Prismafit. A few preliminary applications exist at field strengths of 1.5 T and 7 T. For technical details see methodology.
The basic reference is: M. Uecker, S. Zhang, D. Voit, A. Karaus, K.D. Merboldt, J. Frahm. Real-time MRI at a resolution of 20 ms. NMR Biomed. 23, 986-994 (2010). [Online Version]
Overview:
- Joint Movements
- Wrist
- Oropharyngeal Functions
- Swallowing / Esophageal Function (10 ml Pineapple Juice)
- Cardiovascular Function
- Quantitative Blood Flow - Velocity-Encoded Phase-Contrast MRI
- Quantitative T1 Mapping
- Rapid Volume Coverage
- Interactive Real-time MRI
- 3D Localization in Real Time - Spatially Encoded Phase-Contrast MRI
Joint Movements
Temporomandibular: Opening and Closing of the Mouth.
Experimental details: RF-Spoiled / Refocused Radial FLASH , 0.75 × 0.75 × 5 mm3, acquisition time 66.7 ms, 15 frames per second
Experimental details: refocused radial FLASH , 0.75 × 0.75 × 5 mm3, acquisition time 66.7 ms, 15 frames per second
Collaboration: Krohn, Gersdorff, Bürgers, Universitätsmedizin Göttingen
Reference: S Krohn et al, Eur J Radiol http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2016.10.020
Experimental details: RF-Spoiled FLASH , 0.75 × 0.75 × 8 mm3, acquisition time 2 x 50.0 ms, 2 x 10 frames per second
Collaboration: Krohn, Universitätsmedizin Göttingen, NORAS MRI products GmbH, Höchberg
Wrist
Experimental details: RF-Spoiled Radial FLASH, 0.75 × 0.75 mm2, total acquisition time 50 ms, 20 frames per second
Collaboration: Seif, Universitätsmedizin Göttingen, NORAS MRI products GmbH, Höchberg
Oropharyngeal Functions
Speaking
Experimental details: RF-Spoiled Radial FLASH, 1.4 × 1.4 × 8 mm3, acquisition time 18.0 ms, 55 frames per second
Nasalization of Vowels
Experimental details: RF-Spoiled Radial FLASH, 1.5 × 1.5 × 10 mm3, acquisition time 33.3 ms, 30 frames per second
Reference: A Niebergall et al, Magn Reson Med 69:477-485, 2013. [Online Version]
Stuttering
Experimental details: RF-Spoiled Radial FLASH, 1.4 × 1.4 × 8 mm3, acquisition time 18.0 ms, 55 frames per second
Collaboration: Sommer, Universitätsmedizin Göttingen
Singing and Horn Playing
Experimental details: Radial FLASH, 1.5×1.5×10.0 mm3.
References:
Iltis, Peter W., et al., Human Movement Science 42 (2015): 132-145.[Online Version]
Iltis, Peter W., et al., Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery 5.3 (2015): 374-381.[Online Version]
Collaboration: PW Iltis, Boston; E Altenmüller, Hannover
Swallowing / Esophageal Function (10 ml Pineapple Juice)
Experimental details: RF-Spoiled Radial FLASH, 1.3 × 1.3 × 8 mm3, acquisition time 40.0 ms, 25 frames per second.
References:
A Olthoff et al, "On the physiology of normal swallowing as revealed by magnetic resonance imaging in real time." Gastroenterology research and practice 2014. [Online Version]
A Olthoff et al, Evaluation of dysphagia by novel real-time magnetic resonance imaging. Neurology. [Online Version]
Collaboration: Olthoff, Beham & Ghadimi, Universitätsmedizin Göttingen
Experimental details: RF-Spoiled Radial FLASH, 1.3 × 1.3 × 8 mm3, acquisition time 40.0 ms, 25 frames per second
Collaboration: Olthoff, Beham & Ghadimi, Universitätsmedizin Göttingen
Experimental details: RF-Spoiled Radial FLASH, 1.3 × 1.3 × 8 mm3, acquisition time 40.0 ms, 25 frames per second
Reference: Zhang, S., et al. "Diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease using real-time magnetic resonance imaging."
Scientific Reports (2015). [Online Version]
Collaboration: Olthoff, Beham & Ghadimi, Universitätsmedizin Göttingen
Cardiovascular Function
For recent overview about real-time MRI of cardiovascular functon see
"Real-time magnetic resonance imaging of cardiac function and flow — recent progress".
Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2014 Oct; 4(5): 313–329. [Online Version]
Experimental details: RF-Spoiled Radial FLASH, 1.6 × 1.6 × 6 mm3, acquisition time 33.3 ms, 30 frames per second.
Valsalva Manoeuver
Experimental details: RF-Spoiled Radial FLASH, 1.6 × 1.6 × 6 mm3, acquisition time 33.3 ms, 30 frames per second.
55 & 100 frames per second
Experimental details: RF-Spoiled Radial FLASH, 1.6 × 1.6 × 6 mm3, acquisition time 18.0 / 10.0 ms, 55 / 100 frames per second.
Experimental details: Fully Balanced Radial FLASH, 1.6 × 1.6 × 6 mm3, acquisition time 33.3 ms, 30 frames per second.
Atrial Fibrillation
Experimental details: Radial bSSFP, 1.6 × 1.6 × 6 mm3, acquisition time 33.3 ms, 30 frames per second.
Quantitative Blood Flow - Velocity-Encoded Phase-Contrast MRI
Ascending Aorta, Venc = 200 cm s-1
Experimental details: RF-Spoiled Radial FLASH, 1.3 × 1.3 × 6 mm3, acquisition time 40.0 ms, 25 frames per second.
Reference: AA Joseph et al, NMR Biomed (2012) [Online Version]
Aortic Valve Insufficiency & Stenosis, Venc = 300 cm s-1
Experimental details: RF-Spoiled Radial FLASH, 1.5 × 1.5 × 6 mm3, acquisition time 35.7 ms, 28 frames per second.
Reference: Untenberger et al, Magn Reson Med (2015) [Online Version]
Model-Based Reconstruction
Experimental details: RF-Spoiled Radial FLASH, 1.5 × 1.5 × 6 mm3, acquisition time 25.6 ms, 39 frames per second.
Reference: Tan et al, Magn Reson Med 77:1082-1093, 2017 [Online Version]
Blood Flow and Muscle Movement, Venc = 40 cm s-1
Experimental details: RF-Spoiled Radial FLASH, 1.0 × 1.0 × 4 mm3, acquisition time 50 ms, 20 frames per second.
Reference: AA Joseph et al, Real-time MRI of deep venous flow during muscular exercise. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. [Online Version]
Collaboration: NORAS MRI products GmbH, Höchberg
CSF Flow Through 3rd Ventricle: Repetitive Inspiration (2.5 s)
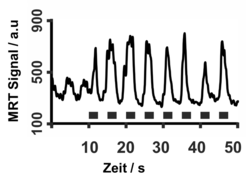
Experimental details: RF-Spoiled Radial FLASH, 0.75 × 0.75 × 5 mm3, acquisition time 50 ms, 20 frames per second.
Reference: S Dreha-Kulaczewski et al, J Neurosci 35:2485-2491 (2015) [Online Version]
Quantitative T1 Mapping
Single-Shot T1 Mapping (inversion recovery)
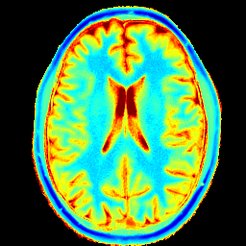
Radial IR-FLASH, 0.75 × 0.75 × 6 mm3, acquisition time 81.5 ms per frame, measurement time 4 s.
Experimental details: RF-Spoiled Radial FLASH, 0.5 × 0.5 × 5 mm3, 64 ms per frame, measuring time 4 s.
References:
X Wang et al, The Open Med Imaging J 9:1-8, 2015 [Online Version]
Hofer, Sabine, et al., Frontiers in Neuroanatomy 9 (2015). [Online Version]
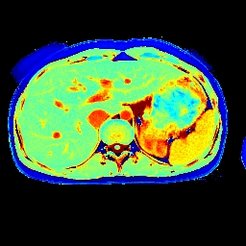
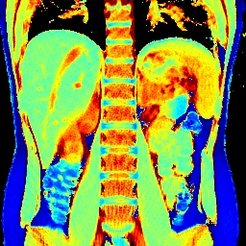
Radial IR-FLASH, 1.3 × 1.3 × 8 mm3, acquisition time 61 ms per frame, measurement time 4 s.
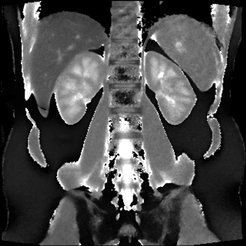

RF-Spoiled Radial FLASH,1.0 × 1.0 × 8 mm3, 43 ms per frame, measuring time 4 s
Reference: X Wang et al, The Open Med Imaging J 9:1-8, 2015 [Online Version]
Cardiac T1 mapping with automatic masking of systolic frames

Radial IR-FLASH, 1.0 × 1.0 × 6 mm3, acquisition time 43 ms per frame, measurement time 3 s per section
References: X Wang et al, High-resolution myocardial T1 mapping using single-shot inversion-recovery fast low-angle shot MRI with radial undersampling and iterative reconstruction, Br J Radiol. [Online Version]
Rapid Volume Coverage
Radial FLASH, 1.0 x 1.0 x 4.0 mm3, automatic slice shift 0.8 mm, acquisition time 67 ms, 15 frames per second
Interactive Real-time MRI
Interactive slice positioning during real-time measurement of the human brain
Experimental details: RF-Spoiled Radial FLASH, 1.8 × 1.8 × 6 mm3, acquisition time 33.3 ms, 30 frames per second
Interactive slice positioning during real-time measurement of the human heart
Experimental details: RF-Spoiled Radial FLASH, 2.3 × 2.3 × 6 mm3, acquisition time 33.3 ms, 30 frames per second
3D Localization in Real Time - Spatially Encoded Phase-Contrast MRI
Real-time 3D MRI of a water-filled tube at 44 ms temporal resolution or 23 frames per second
Experimental details: spatially encoded phase-contrast Radial FLASH, 1.5×1.5 mm2, total acquisition time 44 ms, 23 frames per second
3D Localization of the human hand at 40 ms resolution.
Experimental details: spatially encoded phase-contrast radial FLASH, 2 × 2 mm2, total acquisition time 40 ms, 25 frames per second
Reference: KD Merboldt et al, Magn Reson Med 66, 950-956 (2011) [Online Version]







