Manipulating blood-brain barrier permeability for CNS drug delivery
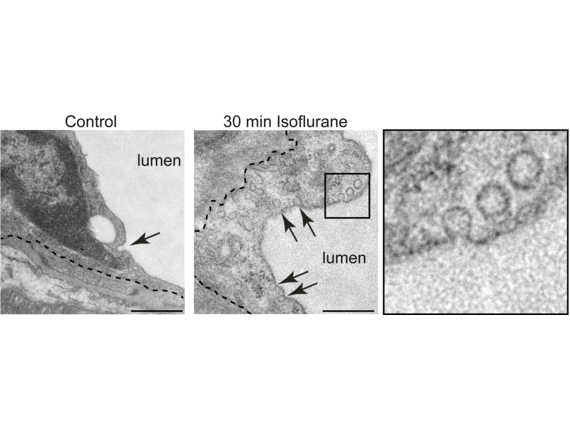
Pharmaceutical intervention in the CNS is hampered by the shielding function of the blood-brain barrier (BBB). We found that the volatile anesthetics increase BBB permeability in a dose-dependent manner. Mechanistically isoflurane disturbs the organization of membrane lipid nanodomains and triggers caveolar transport across the BBB. In a therapeutic glioblastoma trial in mice, simultaneous exposure to isoflurane and cytotoxic agent improves efficacy of chemotherapy.